
Malware Infection
Malware infections occur when malicious software makes its way on to a device or network.
Behaviours

Reporting security incidents
Reporting known or suspected security incidents helps protect the workplace. If the incident is reported early, IT ...

Asking for help
Asking for help can help people learn. Security professionals can advise on how best to approach and resolve ...

Completing security awareness training
Security Awareness training is an important part of organisational security. Completing awareness training ensures ...
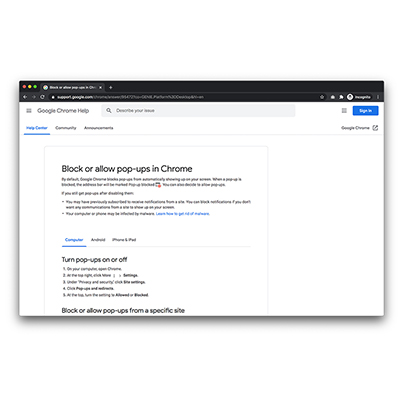
Blocking pop-ups
Most web browsers come with a range of security options. One option is to automatically block pop-ups. Enabling ...

Adding security extensions to browsers
Security/Privacy extensions can increase the security and privacy of a web browser. Extensions such as uBlock ...
Downloading content from trusted websites
Downloading content from untrusted sites increases the threat of malware. Only downloading content from verified ...
![Closing pop-ups with [alt]+[F4] (Windows) or [cmd]+[w] (Mac)](/research/security-behaviour-database/social/behaviours/closing-pop-ups-with-alt-f4-windows-or-cmdw-mac.jpg)
Closing pop-ups with [alt]+[F4] (Windows) or [cmd]+[w] (Mac)
Some malicious pop-up windows display “x” symbols within the window. This is to trick people into clicking the ...

Installing antivirus on workplace devices
Antivirus/Endpoint protection programs provide excellent coverage against known online threats. They should be ...

Enabling firewalls
A firewall is a set of virtual rules that help prevent malicious applications from communicating with a device. ...

Enabling auto-updates
Software updates reduce exposure to known security vulnerabilities. Most devices can be set to auto-update when ...
Enabling Google Play Protect
Google Play Protect should be enabled on all Android devices. With Google Play Protect enabled, apps downloaded ...

Restricting administrator privileges
User accounts have fewer privileges than administrator accounts. User accounts deny malware escalated permissions. ...

Downloading apps from trusted app stores
Apps can hide malware. Trusted app stores such as Google Play and The App Store scan apps for malware, helping to ...

Enabling "show file extensions"
Malicious files are often made to look like other files types so that they are more likely to be opened (.pdf, ...

Following security warnings
Security warning alert to potential harmful activity, like when a malicious website is visited. The advice should ...
Running antivirus if a new icon or desktop pop-up appears
Unexpected icons or pop-ups on a computer’s desktop can indicate malware. Running an antivirus scan can help ...

Doesn't plug unknown devices into work devices
Malicious USB (or other plug-in) devices can be used in cyber attacks. They can be used to upload malware, steal ...

Referring suspicious attachments
Email attachments can contain malware. A supervisor, the IT team or other relevant person should be made aware of ...
Checks websites for signs of deception
Websites can be malicious. Checking for malicious characteristics, such as irregularities in the URL, decreases ...
Using bookmarked websites
Links can be malicious. Bookmarking frequently used websites provides a safer access path.

Doesn't click links in unexpected texts
Criminals will often use instant messaging as an attack vector. Unexpected messages should always be checked for ...

Verifying messages
Contact details can be spoofed. Receiving a message that breaks any norms should be met with suspicion. Using ...

Checking emails before forwarding them
Messages from workplace contacts are more likely to be trusted than messages from other sources. Forwarding ...

Reporting suspicious messages
Suspicious messages received via email, text or phone should be reported to a single point of contact. This allows ...

Checking emails for signs of deception
Criminals will often use emails as an attack vector. Unexpected emails should always be checked for malicious ...
Case study
Magellan Health
In April 2020, cyber criminals hit Fortune 500 company Magellan Health with a double whammy.
Initially, criminals sent Magellan Health employees an email containing a malicious link. Some employees clicked the link. This gave criminals access to a corporate server. They then stole people’s addresses, employee ID numbers, and social security numbers.
Five days later, the criminals launched a ransomware attack. This stopped Magellan Health from being able to access their data.
In a statement to the employees, Magellan Health announced it would be taking company-level measures to prevent similar future incidents. In particular, it stressed the importance of raising cyber security concerns about suspicious emails and phishing scams.
Lion
In June 2020, Australian Brewing giant Lion fell prey to a series of phishing and ransomware attacks.
Criminals first gained control of Lion’s systems and data. Then they demanded a ransom for revocation. No personal or financial information was stolen, but the ransomware caused a system shutdown. This resulted in stock shortages and other business losses.
Lion worked with IT and security professionals to bring systems back online safely, but it took a long time before they could resume normal business.
When asked about the incident, Australian Prime Minister Scott Morrison advised corporate organisations to keep up to date with the latest cyber threat advice, patch internet-facing devices properly and set up Multi-Factor Authentication systems for work equipment.
Android Users, 2018
In 2018, Android users in South Korea were the targets of a sophisticated malware attack. The malware was hiding in plain sight – in seemingly harmless mobile apps.
The malware intercepted bank texts. It also recorded customer calls to financial organisations. By late 2018, the malwae was even redirecting people’s calls: victims who tried to call their banks were redirected to criminals and tricked into handing over sensitive information.
The malware was found to enter the Android systems through 22 apps downloaded from “alternative” app stores. Downloading one of the infected apps set the malicious chain in motion.
Android users can prevent such attacks by: only downloading apps from the Google Play Store; checking app permissions; and regularly updating their Android software.